Seventh Grade Curriculum
- 7 courses included
- 14-day satisfaction guarantee*
- Update grade level anytime
Subscribe more students, save more!
10% off
2 students
20% off
3-5 students
25% off
6+ students
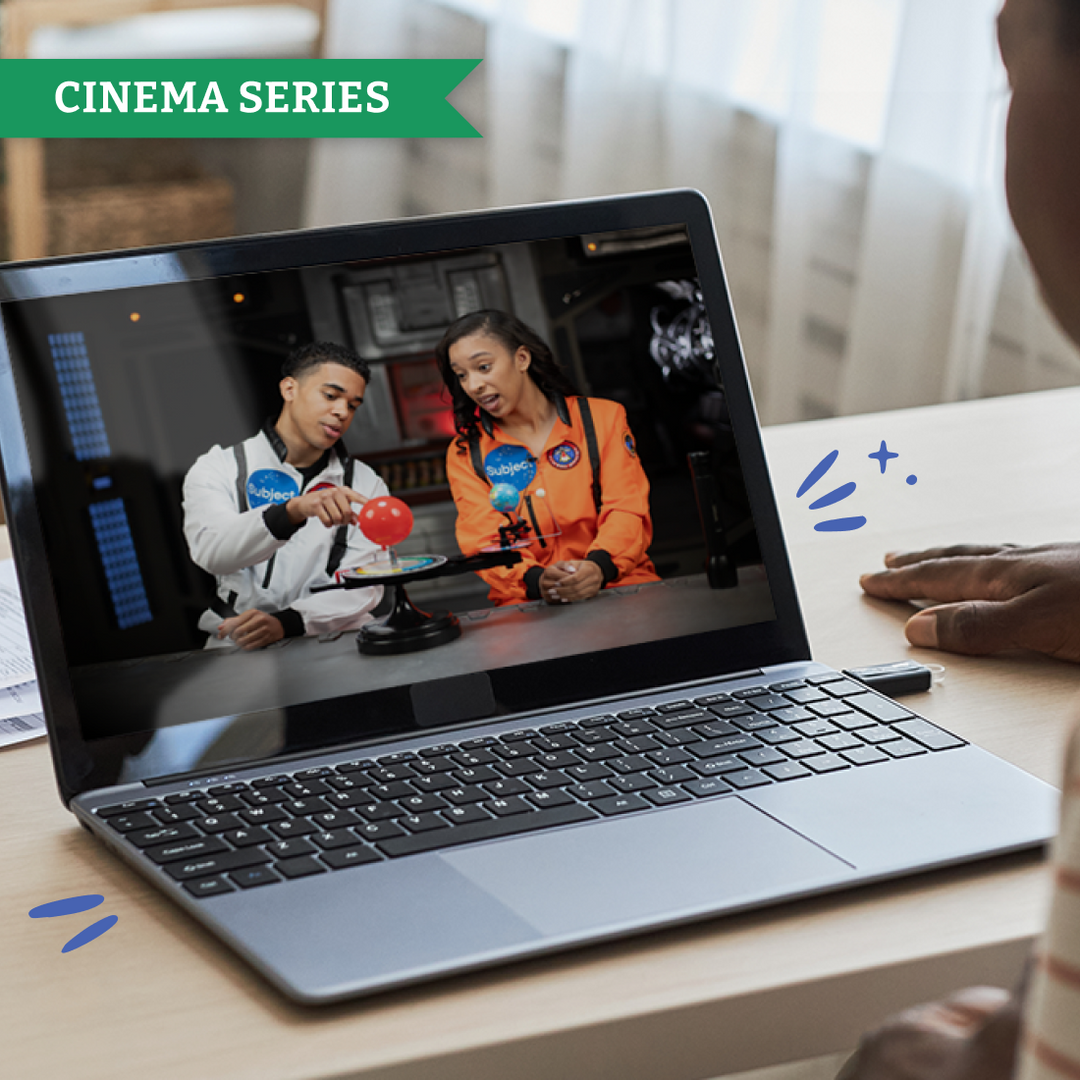
Designed for the way modern preteens learn, our Cinema Series seventh grade curriculum offers story-driven instruction, relatable teachers and short form visual content to maximize engagement. Your seventh grader is enhancing their critical thinking skills while becoming more adept at reasoning and analyzing information.
In english, seventh graders focus on classical literary analysis. In math, seventh graders will dive deep into algebraic and geometric concepts.
Seventh graders have several options to choose from for science, social studies and electives courses. This gives them the opportunity to customize their schedule.
Most popular science and social studies classes for seventh graders:
- Earth Space Science - Develop scientific inquiry and explore geology, oceanography, meteorology, and astronomy.
World Culture & Geography - Dive deep into global cultures and the historical factors that have shaped the world around them.
Seventh graders choose from the following elective options:
- Introduction to Art
- Learning Strategies
- Introduction to Public Speaking & Communication
- Environmental Science
- Digital Media Literacy
Science Alternatives:
- Physical Science
- Life Science
- Environmental Science
History Alternatives:
- United States History
- Ancient World History
English 7
Unit 1: Language Builds Connections
Chapter 1: Understanding Narrative Structure
Chapter 2: Establishing Point of View
Chapter 3: Using Dialogue to Build Connections
Chapter 4: Sensory Language and Description
Chapter 5: Figurative Language and Meaning
Chapter 6: Analyzing Allusions
Chapter 7: Identifying and Comparing Narrative Styles
Chapter 8: Using Textual Evidence
Chapter 9: Theme and Central Idea
Chapter 10: Sound Devices in Poetry
Chapter 11: Brainstorming and Planning a Narrative
Chapter 12: Writing a Narrative Introduction
Chapter 13: Developing Characters and Dialogue
Chapter 14: Structuring a Narrative with Transitions
Chapter 15: Adding Descriptive Details and Figurative Language
Chapter 16: Writing a Narrative Conclusion
Unit 2: The Power of Argument
Chapter 1: Identifying Claims and Arguments
Chapter 2: Understanding Audience in Arguments
Chapter 3: Understanding Ethos (Credibility in Arguments)
Chapter 4: Understanding Pathos (Emotional Appeals in Arguments)
Chapter 5: Understanding Logos (Logical Reasoning in Arguments)
Chapter 6: Citing Textual Evidence to Support Analysis
Chapter 7: Evaluating an Author's Purpose in Arguments
Chapter 8: The Power of Word Choice and Tone in Persuasion
Chapter 9: Writing a Strong Thesis Statement and Introduction
Chapter 10: Using Transitions for Clarity and Flow
Chapter 11: Strengthening Counterarguments and Rebuttals
Chapter 12: Writing a Strong Conclusion
Chapter 13: Outlining a Full Argumentative Essay
Chapter 14: Drafting and Revising an Argumentative Essay
Chapter 15: Editing for Clarity and Formal Style
Chapter 16: Publishing and Presenting an Argument
Unit 3: Language is a Tool for Exploration
Chapter 1: Analyzing Exploration as a Theme
Chapter 2: Exploring Setting and Its Role in Discovery
Chapter 3: Understanding Point of View in Exploration Stories
Chapter 4: Comparing Fictional Exploration to Historical Accounts
Chapter 5: Exploring Themes of Justice in Exploration Stories
Chapter 6: Using Precise Language in Informative Writing
Chapter 7: Creating Cohesion with Transitions
Chapter 8: Analyzing Figurative Language in Exploration Stories
Chapter 9: Developing Ideas with Supporting Details
Chapter 10: Brainstorming and Planning an Informative Essay
Chapter 11: Writing a Strong Introduction
Chapter 12: Developing the Body with Facts and Examples
Chapter 13: Using Domain-Specific Vocabulary
Chapter 14: Creating Cohesion with Transitions
Chapter 15: Writing a Strong Conclusion
Chapter 16: Editing and Publishing
Unit 4: Information in Action
Chapter 1: Exploring Figurative Language in Songs
Chapter 2: Understanding Theme in Movies
Chapter 3: Analyzing Point of View in Social Media
Chapter 4: Exploring Symbolism in Everyday Objects
Chapter 5: Comparing Themes Across Music and Texts
Chapter 6: Developing Literary Comparisons through Characters and Pop Culture
Chapter 7: Crafting Descriptive Writing Inspired by Photos
Chapter 8: Rewriting Endings for Modern Audiences
Chapter 9: Exploring Parody and Satire
Chapter 10: Visual Storytelling: Graphic Novels and Comics
Chapter 11: Exploring Foreshadowing
Chapter 12: Creative Retellings
Chapter 13: Exploring Imagery Through Poetry
Chapter 14: Analyzing Irony in Literature
Chapter 15: Comparing Film Adaptations to Texts
Chapter 16: Advocacy Across Media
Math 7
Unit 1: Integer Operations with Rational Numbers
Chapter 1: Zero Pairs
Chapter 2: Representing Integers on a Number Line
Chapter 3: Adding and Subtracting Integers
Chapter 4: Absolute Value as Distance
Chapter 5: Representing Fractions on a Number Line
Chapter 6: Adding and Subtracting Fractions
Chapter 7: Multiplying and Dividing Integers
Chapter 8: Multiplying Fractions
Chapter 9: Dividing Fractions
Chapter 10: Converting Fractions, Decimals, and Percents
Chapter 11: Exponents with Negative Rational Bases
Chapter 12: Order of Operations
Unit 2: Ratios and Proportional Relationships
Chapter 1: Identifying Proportional Relationships
Chapter 2: Identifying Graphs as Proportional Relationships
Chapter 3: Constant of Proportionality from Tables
Chapter 4: Constant of Proportionality from Graphs
Chapter 5: Solving Proportional Equations
Chapter 6: Interpreting Equations of Proportional Relationships in Context
Chapter 7: Unit Rates
Chapter 8: Percentages with Tip and Tax
Chapter 9: Commission and Percent Markup
Unit 3: Expressions and Equations
Chapter 1: Expressions vs. Equations
Chapter 2: Combining Like Terms
Chapter 3: Distributive Property
Chapter 4: Finding Equivalent Expressions
Chapter 5: Solving Two-Step Equations
Chapter 6: Interpreting and Solving Two-Step Equations in Context
Chapter 7: Solving and Graphing One-Step Inequalities
Chapter 8: Solving and Graphing Two-Step Inequalities
Unit 4: Geometry
Chapter 1: Scale Drawings and Scale Factors
Chapter 2: Constructing Scale Copies
Chapter 3: Area and Circumference of Circles
Chapter 4: Area of Compound Shapes
Chapter 5: Area of Shaded Sections
Chapter 6: Identifying Types of Angle Relationships
Chapter 7: Finding Missing Angles
Chapter 8: Triangle Inequality Theorem
Chapter 9: Volume and Surface Area of Prisms
Chapter 10: Volume and Surface Area of Pi-Based Shapes
Unit 5: Probability and Statistics
Chapter 1: Simple Probability
Chapter 2: Theoretical vs. Experimental Probability
Chapter 3: Making Predictions with Probability
Chapter 4: Sample Space for Compound Events
Chapter 5: Probability of Compound Events with Modeling
Chapter 6: Sampling Populations
Chapter 7: Making Inferences About a Population
Chapter 8: Comparing Distributions
World Culture and Geography
Unit 1: The Explorer's Toolkit – Geographic Skills to Understand the World
Chapter 1: Mapping Our World: Tools and Perspectives
Chapter 2: Data Detectives: Investigating Geographic Sources
Chapter 3: The Five Themes of Geography
Unit 2: The United States and Canada
Chapter 1: The Physical Geography and Climate of the U.S. and Canada
Chapter 2: Settlement Patterns and Ways of Life in the U.S. and Canada
Chapter 3: Indigenous Peoples of the U.S. and Canada
Chapter 4: Water Scarcity and Conservation in the U.S. and Canada
Chapter 5: Urbanization and the Growth of Megacities
Unit 3: Latin America
Chapter 1: The Physical Geography and Climate of Latin America
Chapter 2: Settlement Patterns and Ways of Life in Latin America
Chapter 3: Early Civilizations of Latin America
Chapter 4: Deforestation and Environmental Challenges in the Amazon Rainforest
Chapter 5: Climate Migration in Latin America
Unit 4: Africa
Chapter 1: The Physical Geography and Climate of Africa
Chapter 2: Settlement Patterns and Ways of Life in Africa
Chapter 3: From Desert to Rainforest: How African Cultures Adapted and Thrived
Chapter 4: Wildlife Conservation in Africa
Chapter 5: Africa's Role in Global Trade
Unit 5: Southwest and Central Asia
Chapter 1: The Physical Geography and Climate of Southwest Asia
Chapter 2: Settlement Patterns and Ways of Life in Southwest Asia
Chapter 3: Civilizations and Cultures of Southwest and Central Asia
Chapter 4: Oil, Trade, and Global Influence in Southwest Asia
Chapter 5: Liquid Gold: Managing Water Resources in Southwest and Central Asia
Unit 6: Monsoon Asia
Chapter 1: The Physical Geography and Climate of Monsoon Asia
Chapter 2: Settlement Patterns and Ways of Life in Monsoon Asia
Chapter 3: Cultural Crossroads: How Religion, Trade, and Ideas Shaped Asian Civilizations
Chapter 4: China's Belt and Road Initiative
Chapter 5: Japan's Aging Population
Unit 7: Europe and Russia
Chapter 1: The Physical Geography and Climate of Europe and Russia
Chapter 2: Settlement Patterns and Ways of Life in Europe and Russia
Chapter 3: Civilizations and Cultures of Europe and Russia
Chapter 4: The European Union – Cooperation, Trade, and Challenges
Chapter 5: Energy Resources and the Russia-Europe Connection
Unit 8: Antarctica and Oceania
Chapter 1: The Physical Geography and Climate of Antarctica and Oceania
Chapter 2: Settlement Patterns and Ways of Life in Antarctica and Oceania
Chapter 3: Island Nations and Indigenous Cultures: The People of Oceania
Chapter 4: Rising Sea Levels in Oceania
Chapter 5: Scientific Research and Environmental Protection in Antarctica
You're absolutely right, Micaela—we were just about to finish with Earth Science when the message cut off. Here's the final section to complete the Seventh Grade Core Course Scope & Sequence, starting where we left off:
Earth Science
Unit 1: Earth in Space
Chapter 1: Observing Patterns in the Sky
Chapter 2: The Sun and Earth
Chapter 3: The Moon and Earth
Chapter 4: The Earth-Sun-Moon System
Chapter 5: Seasons on Earth
Chapter 6: Solar Eclipses
Chapter 7: Lunar Eclipses
Chapter 8: Gravity
Chapter 9: The Solar System
Chapter 10: The Formation of Our Solar System
Chapter 11: The Milky Way Galaxy
Chapter 12: Final Mission – Beyond the Milky Way Galaxy
Unit 2: The Geologic Timescale
Chapter 1: Introduction to the Geologic Timescale
Chapter 2: Rock Layers
Chapter 3: Relative Dating
Chapter 4: The Fossil Record
Chapter 5: Continental Drift
Chapter 6: The Seafloor
Chapter 7: Major Earth Events
Chapter 8: Final Mission – Protecting Earth from Cosmic Threats
Unit 3: Plate Tectonics and Rock Cycling
Chapter 1: Earth's Changing Surface
Chapter 2: Tectonic Plates and Earth's Interior
Chapter 3: Tectonic Plate Boundaries
Chapter 4: Earthquakes and Volcanoes
Chapter 5: Seafloor Spreading
Chapter 6: Rock Cycling
Chapter 7: Surface Processes – Weathering, Erosion, and Deposition
Chapter 8: Final Mission – Geologic Processes Beyond Planet Earth
Unit 4: Weather and Climate
Chapter 1: Introduction to Weather and Climate
Chapter 2: Earth's Spheres
Chapter 3: Water Cycling
Chapter 4: Clouds and Precipitation
Chapter 5: Air Masses and Weather Fronts
Chapter 6: Wind Patterns
Chapter 7: Ocean Currents
Chapter 8: Extreme Weather Events
Chapter 9: Climate Zones on Earth
Chapter 10: Weather Forecasts and Climate Projection
Unit 5: Natural Hazards
Chapter 1: Observing Natural Hazards
Chapter 2: Causes of Natural Hazards
Chapter 3: Forecasting Natural Hazards
Chapter 4: Earthquakes and Engineering Design Solutions
Chapter 5: Tsunamis
Chapter 6: Hurricanes
Chapter 7: Earth's Changing Climate and Natural Hazards
Chapter 8: Floods and Engineering Solutions
Chapter 9: Final Mission – Creating a Hazard Preparedness Plan
Unit 6: Natural Resources and Human Impact
Chapter 1: Melting Polar Ice and Glaciers
Chapter 2: Distribution of Resources on Earth
Chapter 3: Rising Global Temperatures
Chapter 4: Human Resource Consumption and Impact on Earth's Systems
Chapter 5: Evaluating Solutions to Minimize Human Impact
Chapter 6: Optimizing Solutions to Minimize Human Impact
Chapter 7: The Future of Earth's Climate and Natural Resources
Chapter 8: Final Mission – Advising the Space Traveler